GRK2 inhibits Flt-1+ macrophage infiltration and its proangiogenic properties in rheumatoid arthritis: Study
A publication from Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B discusses how GRK2 inhibits Flt-1+ macrophage infiltration and its proangiogenic properties in rheumatoid arthritis.
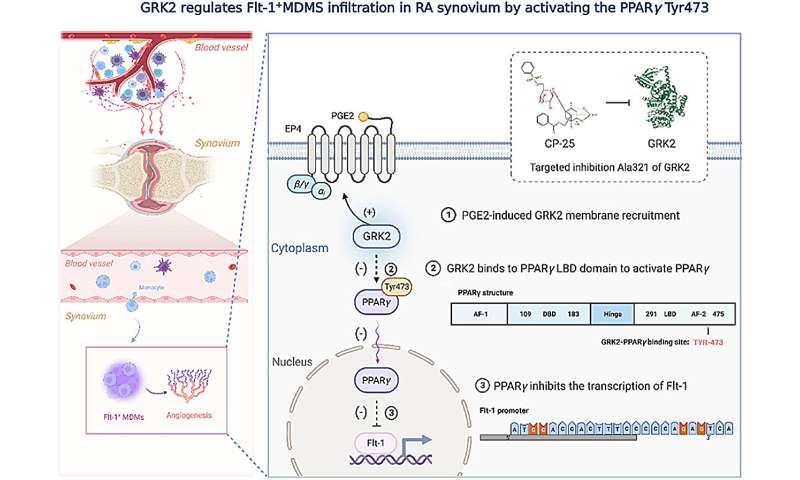
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease with a complex etiology. Monocyte-derived macrophage (MDM) infiltration is associated with RA severity. The authors of this article report the deletion of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) reprograms macrophages toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype by recovering G-protein-coupled receptor signaling.
However, as more GRK2-interacting proteins were discovered, the GRK2 interactome mechanisms in RA have been understudied. Thus, in the collagen-induced arthritis mouse model, we performed genetic GRK2 deletion using GRK2f/fLyz2-Cre+/− mice. Synovial inflammation and M1 polarization were improved in GRK2f/fLyz2-Cre+/− mice.
Supporting experiments with RNA-seq and dual-luciferase reporter assays identified peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) as a new GRK2-interacting protein. It was further confirmed that fms-related tyrosine kinase 1 (Flt-1), which promoted macrophage migration to induce angiogenesis, was inhibited by GRK2-PPARγ signaling. Mechanistically, excess GRK2 membrane recruitment in CIA MDMs reduced the activation of PPARγ ligand-binding domain and enhanced Flt-1 transcription.
Furthermore, the treatment of mice with GRK2 activity inhibitor resulted in significantly diminished CIA pathology, Flt-1+ macrophages induced-synovial inflammation, and angiogenesis. Altogether, it is anticipated to facilitate the elucidation of previously unappreciated details of GRK2-specific intracellular signaling. Targeting GRK2 activity is a viable strategy to inhibit MDMs infiltration, affording a distinct way to control joint inflammation and angiogenesis of RA.
More information:
Xuezhi Yang et al, GRK2 inhibits Flt-1+ macrophage infiltration and its proangiogenic properties in rheumatoid arthritis, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.09.013
Provided by Compuscript Ltd